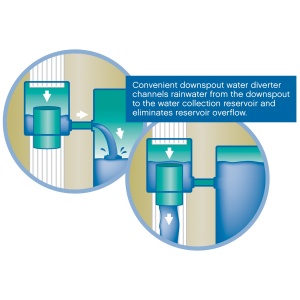
Rainwater Harvesting
Showing all 33 results
-
Downspout Diverter Kit with 39 Inch Hose – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$37.99 -
Downspout Rainwater Collection Colander System Filter 2″ x 3″ (White) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$40.99 -
Downspout Rainwater Collection Diverter with Filter 3″ x 4″ (White) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$42.99 -
EMSCO Group Deluxe Rain Barrel Downspout Diverter Kit – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$41.99 -
FCMP Outdoor Rain Barrel (Grey) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$189.99 -
FCMP Outdoor Wood Grain Rain Barrel (Brown) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$167.99 -
GROW1 26 Gallon Collapsible Reservoir Water Tank – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$114.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Rain Water Tank (200 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$338.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Reservoir Water Tank – 105 Gallon – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$230.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Reservoir Water Tank (60 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$146.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Reservoir Water Tank 13 Gallon – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$92.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Reservoir Water Tank 132 Gallon – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$242.99 -
LINSHI Portable Large-Capacity Water Storage Bag (110L) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$145.99 -
Minimprover Quarter Turn Spigot (2-Pack) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$45.99 -
Minimprover Spigot, 3/4″Male G Threaded to 3/4″ Male GHT – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$32.99 -
NDS (50 Gallon) Rainwater Collection System Kit with 3 Side Panels and 1 Cover (Black) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$222.99 -
Oatey Mystic Hose and Plug Replacement Kit – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$28.99 -
Oatey Mystic™ Rainwater Collection System (White) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$39.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rain Barrel 3/4” Hose 66 Gallon with Zipper Dark Green – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$87.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rainwater Barrel – 53 Gallon with Zipper (Dark Green) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$84.99 -
Algreen Athena (50 Gallon) Plastic Rain Water Collection Drum – Brownstone (2 Pack) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$484.99 -
Good Ideas Rain Wizard 50 Gallon Plastic Rain Barrel Water Collector with Brass Spigot, Oak (2 Pack) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$461.99 -
GROW1 Collapsible Rain Water Storage Tank (265 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$480.99 -
Lostronaut Collapsible Rainwater Barrel (26 Gallon) with Two Spigots and Overflow Kit – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$64.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rain Barrel Dark Green (100 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$87.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rain Water Barrel – 42 Gallon with Filter (Green) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$72.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rain Water Collection Barrel – 3/4 ” Hose 66 Gallon with Filter (Light Green) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$59.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rainwater Collection barrel (66 Gallon – Black) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$92.99 -
RIOBOW Collapsible Rainwater Collection System (100 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$59.99 -
RIOBOW Rain Barrels Rainwater Collection System – 53 Gallon with Zipper (Black) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$92.99 -
RIOBOW Rain Water Collection Barrel (100 Gallon) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$100.99 -
RIOBOW Rain Water Collection System 3/4” Hose – 26 Gallon (Green) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$59.99 -
ZROYbmu 2023 Latest Version Upgraded Rainwater Collection System for 2″ X 3″, 3″ X 4″ (White) – (SHIPS IN 1-2 WEEKS)
$72.99
Rainwater Harvesting: A Comprehensive Guide
 At Prep SOS, we are committed to helping you save water and money while protecting the environment. One of the most effective ways to achieve these goals is through rainwater harvesting. In this guide, we will provide you with all the information you need to get started with rainwater harvesting, including its benefits, types of systems, components, design, installation, maintenance, and regulations.
At Prep SOS, we are committed to helping you save water and money while protecting the environment. One of the most effective ways to achieve these goals is through rainwater harvesting. In this guide, we will provide you with all the information you need to get started with rainwater harvesting, including its benefits, types of systems, components, design, installation, maintenance, and regulations.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable and cost-effective way to reduce your dependence on municipal water, which can be limited, expensive, or of poor quality. By capturing and using rainwater, you can:
- Save money on water bills and irrigation costs
- Reduce stormwater runoff and flooding
- Improve soil moisture and plant growth
- Enhance water security and resilience
- Minimize water pollution and erosion
- Promote biodiversity and green infrastructure
Types of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
There are two main types of rainwater harvesting systems: above-ground and below-ground. Each has its advantages and disadvantages depending on the site, climate, and intended use.
Above-Ground Systems
Above-ground systems are typically easier and cheaper to install and maintain than below-ground systems. They can include:
- Rain barrels: These are small containers (usually 50-100 gallons) that collect rainwater from rooftops via downspouts. They can be used for outdoor watering, car washing, or other non-potable uses.
- Cisterns: These are larger containers (usually 500-10,000 gallons) that store rainwater for various uses, such as toilet flushing, laundry, or fire protection. They can be made of different materials (e.g., plastic, concrete, metal) and shapes (e.g., round, rectangular, underground).
- Tanks: These are intermediate-size containers (usually 100-500 gallons) that can be used for similar purposes as cisterns, but with more flexibility in placement and mobility.
Below-Ground Systems
Below-ground systems are typically more expensive and complex to install and maintain than above-ground systems. They can include:
- Infiltration basins: These are shallow excavations that allow rainwater to percolate into the soil slowly. They can improve groundwater recharge and reduce erosion, but may require more space and maintenance than other systems.
- Dry wells: These are deep excavations that store rainwater temporarily and release it slowly into the soil or a drain field. They can be useful in areas with high water tables or limited space, but may require periodic cleaning and inspection.
- In-ground tanks: These are large containers (usually 1,000-50,000 gallons) that can be buried underground for various uses, such as irrigation, cooling, or industrial processes. They can be customized to fit specific needs and can provide significant water savings, but may require more planning and excavation.
Components of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Regardless of the type of system, there are several key components that make rainwater harvesting possible and effective:
- Catchment area: This is the surface (usually a roof) where rainwater falls and can be collected. It should be clean, smooth, and sloped to direct water towards the downspouts.
- Conveyance system: This is the network of gutters, downspouts, pipes, and filters that move rainwater from the catchment area to the storage or infiltration area. It should be sized and designed to handle the expected rainfall and prevent clogging or overflow.
Storage or infiltration area: This is the place where rainwater is stored or infiltrated into the soil. It should be safe, accessible, and durable, and designed to match the intended use and capacity of the system.
- Pump or gravity feed system: This is the mechanism that moves rainwater from the storage or infiltration area to the intended use, such as a hose, sprinkler, or indoor fixture. It should be efficient, reliable, and safe, and designed to match the pressure and flow requirements of the use.
- Treatment and backup system: This is the additional equipment or measures that ensure the quality and safety of the rainwater, such as filtration, disinfection, or backup supply. It should be appropriate for the intended use and comply with the relevant regulations and standards.
Design and Installation of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Designing and installing a rainwater harvesting system requires careful planning, research, and coordination. Here are some steps to follow:
- Assess your water needs and sources: Determine how much water you need for your household, garden, or business, and where you can collect and store rainwater. Consider the size, location, and orientation of your catchment area, and the local climate, soil, and topography.
- Choose the type and size of system: Based on your needs and sources, select the most suitable type and size of system, and decide on the components and features you need. Consult with a professional or a reputable supplier for advice and assistance.
- Obtain permits and approvals: Check with your local authorities for any permits, approvals, or regulations that apply to rainwater harvesting systems, such as building codes, zoning rules, health standards, or environmental permits.
- Prepare the site and components: Clear and level the site where you want to install the system, and prepare the components by cleaning, assembling, and testing them. Ensure that you have the right tools, equipment, and safety gear for the job.
- Install the system: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installing each component, and make sure that they are connected, sealed, and anchored properly. Test the system for leaks, flow, and pressure, and adjust the settings as needed.
- Maintain the system: Regularly inspect, clean, and maintain each component of the system to ensure its proper functioning and longevity. Replace any damaged or worn-out parts, and follow the recommended schedule for maintenance and service.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a simple yet powerful way to conserve water, reduce costs, and protect the environment. By following the tips and guidelines in this guide, you can design, install, and maintain a rainwater harvesting system that meets your needs and exceeds your expectations. Contact us today for more information and support on rainwater harvesting, and start harvesting the benefits of rainwater!